
- •1. TABLE OF CONTENTS
- •2. OVERVIEW
- •3. PROCESS CONTROL
- •3.1 INTRODUCTION
- •3.2 CONTROL SYSTEM CHARACTERISTICS
- •3.3 CONTROLLER TYPES
- •3.4 PROCESS DIAGRAMS AND SYMBOLS
- •3.5 PRACTICE QUESTIONS
- •4. DISCRETE CONTROLLER DESIGN
- •4.1 POSITIONING CONTROLLERS
- •4.1.1 Dead Beat Control
- •4.1.2 Programming Examples
- •4.1.2.1 - BASIC
- •4.1.2.3 - Pascal
- •4.1.2.4 - 6811 Assembler
- •4.1.3 First Order Response
- •4.2 TRACKING
- •4.2.1 Minimum Error
- •4.3 DISTURBANCE RESISTANT
- •4.3.1 Disturbance Minimization
- •4.4 MULTI-CONTROLLER SYSTEMS
- •4.4.1 Disturbance Feedforward
- •4.4.2 Command Feedforward
- •4.4.3 Cascade
- •4.5 SAMPLE TIME
- •4.6 SUMMARY
- •4.7 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •5. DISCRETE SYSTEMS
- •5.1 DISCRETE SYSTEM MODELLING WITH EQUATIONS
- •5.1.1 Getting a Discrete Equation
- •5.1.2 First Order System Example
- •5.1.3 Second Order System Example
- •5.1.4 Example of Dead (Delay) Time
- •5.2 DISCRETE CONTROLLERS
- •5.2.1 A Proportional Controller
- •5.2.2 Integral Control
- •5.2.3 Differential Control
- •5.2.4 Proportional, Integral, Derivative (PID) Control
- •5.3 BLOCK DIAGRAMS AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS
- •5.3.1 The Backward-Shift ‘B’ Operator
- •5.3.2 Reducing Block Diagrams
- •5.3.3 Back-Shift Transform Table
- •5.3.3.1 - A Summary of Differential Equation Solutions
- •5.3.4 Stability
- •5.4 SAMPLING FUNCTIONS
- •5.5 SYSTEM RESPONSE
- •5.6 STEADY STATE ERROR
- •5.7 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •6. PETRI NETS
- •6.1 INTRODUCTION
- •6.2 IMPLEMENTATION FOR A PLC
- •6.3 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •7. CONTINUOUS CONTROL SYSTEMS
- •7.1 CONTROL SYSTEMS
- •7.1.1 PID Control Systems
- •7.1.2 Analysis of PID Controlled Systems With Laplace Transforms
- •7.1.3 Manipulating Block Diagrams
- •7.1.3.1 - Commercial PID Tuners
- •7.1.4 Finding The System Response To An Input
- •7.1.5 System Response
- •7.1.6 A Motor Control System Example
- •7.1.7 System Error
- •7.1.8 Controller Transfer Functions
- •7.2 ROOT-LOCUS PLOTS
- •7.2.1 Approximate Plotting Techniques
- •7.2.2 State Variable Control Systems
- •7.3 DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS CONTROLLERS
- •7.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •8. FUZZY LOGIC
- •8.1 COMMERCIAL CONTROLLERS
- •8.2 REFERENCES
- •8.3 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •9. MECHATRONICS CIRCUITS
- •9.1 POWER SWITCHING
- •9.2 USER INPUT/OUTPUT
- •9.2.1 Multiplexing
- •10. HARDWARE BASED CONTROLLERS
- •10.1 CIRCUITS
- •10.2 FLUIDICS
- •10.3 PNEUMATICS
- •10.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •11. EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
- •11.1 TYPES
- •11.1.1 Micro Controllers
- •11.1.2 DSPs
- •11.1.3 CPUs
- •11.2 CONTROLLER DESIGN EXAMPLE
- •11.3 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •12. DISCRETE SENSORS
- •12.1 INTRODUCTION
- •12.2 SENSOR WIRING
- •12.2.1 Switches
- •12.2.2 Transistor Transistor Logic (TTL)
- •12.2.3 Sinking/Sourcing
- •12.2.4 Solid State Relays
- •12.3 CONTACT DETECTION
- •12.3.1 Contact Switches
- •12.3.2 Reed Switches
- •12.4 PROXIMITY DETECTION
- •12.4.1 Optical (Photoelectric) Sensors
- •12.4.2 Capacitive Sensors
- •12.4.3 Inductive Sensors
- •12.4.4 Ultrasonic
- •12.4.5 Hall Effect
- •12.4.6 Fluid Flow
- •12.4.7 Other Types
- •12.5 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •13. CONTINUOUS SENSORS
- •13.1 INPUT ISSUES
- •13.2 SENSOR TYPES
- •13.3 ANGULAR POSITION
- •13.3.1 Potentiometers
- •13.3.2 Encoders
- •13.3.3 Resolvers
- •13.3.4 Practice Problems
- •13.4 LINEAR POSITION
- •13.4.1 Potentiometers
- •13.4.2 Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDT)
- •13.4.3 Moire Fringes
- •13.4.4 Interferometers
- •13.5 VELOCITY
- •13.5.1 Velocity Pickups
- •13.5.2 Tachometers
- •13.6 ACCELERATION
- •13.6.1 Accelerometers
- •13.7 FORCE/MOMENT
- •13.7.1 Strain Gages
- •13.7.2 Piezoelectric
- •13.8 FLOW RATE
- •13.8.1 Venturi
- •13.9 TEMPERATURE
- •13.9.1 Resistive Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
- •13.9.2 Thermocouples
- •13.9.3 Thermistors
- •13.10 SOUND
- •13.10.1 Microphones
- •13.11 LIGHT INTENSITY
- •13.11.1 Light Dependant Resistors (LDR)
- •13.12 PRESSURE
- •13.12.1 Bourdon Tubes
- •13.13 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •13.14 REFERENCES
- •14. ACTUATORS
- •14.1 ACTUATOR TYPES
- •15. DISCRETE ACTUATORS
- •15.1 INTRODUCTION
- •15.1.1 Interfacing
- •15.1.1.1 - Relays
- •15.1.1.2 - Transistors
- •15.1.1.3 - Triacs
- •15.2 TYPES
- •15.2.1 Solenoids
- •15.2.2 Hydraulic
- •15.2.3 Hydraulics
- •15.2.4 Electric
- •15.2.5 Pneumatic
- •15.2.6 Others
- •15.3 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •16. CONTINUOUS ACTUATORS
- •16.1 ACTUATOR CONTROL
- •16.1.1 Block Diagrams
- •16.1.2 Linear Control Systems
- •16.1.3 Motor Controllers
- •16.1.3.1 - DC Motors
- •16.1.3.2 - Stepper Motors
- •16.1.3.3 - Separately Excited DC Motor
- •16.1.3.4 - AC Motors
- •16.1.3.4.1 - Synchronous
- •16.1.4 Hydraulic
- •16.2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •17. PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS
- •17.1 BASIC PLCs
- •17.1.1 PLC Connections
- •17.1.2 Ladder Logic
- •17.1.3 Ladder Logic Outputs
- •17.1.4 Ladder Logic Inputs
- •17.2 A SIMPLE EXAMPLE
- •17.3 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •18. PLC CONNECTION
- •18.1 SWITCHED INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
- •18.1.1 Input Modules
- •18.1.2 Output Modules
- •18.1.2.1 - Relays
- •18.2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •19. PLC OPERATION
- •19.1 PLC ORGANIZATION
- •19.2 PLC STATUS
- •19.3 MEMORY TYPES
- •19.4 SOFTWARE BASED PLCS
- •19.5 PROGRAMMING STANDARDS
- •19.5.2 The Future of Open Architecture Controllers
- •19.6 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •20. SWITCHING LOGIC
- •20.1 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
- •20.2 DISCRETE LOGIC
- •20.2.1 Boolean Algebra for Circuit and Ladder Logic Design
- •20.2.2 Boolean Forms
- •20.3 SIMPLIFYING BOOLEAN EQUATIONS
- •20.3.1 Karnaugh Maps for Combinatorial Design
- •20.4 ADDITIONAL TOPICS
- •20.4.1 Negative Logic
- •20.4.2 Common Logic Forms
- •20.4.2.1 - NAND/NOR Forms
- •20.4.2.2 - Multiplexers
- •20.4.2.3 - Seal-in Circuits
- •20.5 DESIGN CASES
- •20.5.1 Logic Functions
- •20.5.2 Car Safety System
- •20.5.3 Motor Forward/Reverse
- •20.6 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •21. NUMBERING
- •21.1 INTRODUCTION
- •21.2 DATA VALUES
- •21.2.1 Binary
- •21.2.2 Boolean Operations
- •21.2.3 Binary Mathematics
- •21.2.4 BCD (Binary Coded Decimal)
- •21.2.5 Number Conversions
- •21.2.6 ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
- •21.3 DATA CHARACTERIZATION
- •21.3.1 Parity
- •21.3.2 Gray Code
- •21.3.3 Checksums
- •21.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •22. EVENT BASED LOGIC
- •22.1 INTRODUCTION
- •22.2 TIMERS, COUNTERS, FLIP-FLOPS, LATCHES
- •22.2.1 Latches
- •22.2.2 Flip-Flops
- •22.2.3 Timers
- •22.2.4 Counters
- •22.3 PROGRAM DESIGN METHODS
- •22.3.1 Process Sequence Bits
- •22.3.2 Timing Diagrams
- •22.4 DESIGN CASES
- •22.4.1 Counters And Timers
- •22.4.2 More Timers And Counters
- •22.4.3 Oscillator
- •22.4.4 More Timers
- •22.4.5 Cascaded Timers
- •22.4.6 Deadman Switch
- •22.4.7 Conveyor
- •22.4.8 Accept/Reject Sorting
- •22.4.9 Shear Press
- •22.4.10 Actuator Failure
- •22.4.11 Palm Button Detection
- •22.5 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •23. SEQUENTIAL LOGIC DESIGN
- •23.1 SCRIPTS
- •23.2 FLOW CHARTS
- •23.3 STATE BASED MODELLING
- •23.3.1 State Diagrams Example
- •23.3.1.1 - Block Logic Conversion
- •23.3.1.2 - Single State Equations
- •23.3.1.3 - Entry and Exit State Equations
- •23.3.1.4 - State Transition Equations
- •23.4 PARALLEL PROCESS FLOWCHARTS
- •23.4.1 Implementation with Microcontroller
- •23.5 SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS
- •23.5.1 Latches and Seal-in
- •23.5.2 Shift Registers
- •23.6 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •24. ADVANCED LADDER LOGIC FUNCTIONS
- •24.1 ADDRESSING
- •24.1.1 Data Files
- •24.1.1.1 - Inputs and Outputs
- •24.1.1.2 - User Bit Memory
- •24.1.1.3 - Timer Counter Memory
- •24.1.1.4 - PLC Status Bits (for PLC-5s and Micrologix)
- •24.1.1.5 - User Function Control Memory
- •24.1.1.6 - Integer Memory
- •24.1.1.7 - Floating Point Memory
- •24.2 INSTRUCTION TYPES
- •24.2.1 Basic Data Handling
- •24.2.1.1 - Move Functions
- •24.2.1.2 - Mathematical Functions
- •24.2.2 Logical Functions
- •24.2.2.1 - Comparison of Values
- •24.2.2.2 - Binary Functions
- •24.2.3 Boolean Operations
- •24.2.4 Binary Mathematics
- •24.2.5 BCD (Binary Coded Decimal)
- •24.2.6 Advanced Data Handling
- •24.2.6.1 - Multiple Data Value Functions
- •24.2.7 Complex Functions
- •24.2.7.1 - Shift Registers
- •24.2.7.2 - Stacks
- •24.2.7.3 - Sequencers
- •24.2.8 Program Control Structures
- •24.2.8.1 - Branching and Looping
- •24.2.8.2 - Immediate I/O Instructions
- •24.2.8.3 - Fault Detection and Interrupts
- •24.2.9 Block Transfer Functions
- •24.3 DESIGN TECHNIQUES
- •24.3.1 State Diagrams
- •24.4 DESIGN CASES
- •24.4.1 If-Then
- •24.4.2 For-Next
- •24.4.3 Conveyor
- •24.5 FUNCTION REFERENCE
- •24.6 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •25. PLC PROGRAMMING
- •25.1 PROGRAMMING STANDARDS
- •25.1.2 The Future of Open Architecture Controllers
- •25.2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •26. STRUCTURED TEXT PROGRAMMING
- •26.1 INTRODUCTION
- •26.2 THE LANGUAGE
- •26.3 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •27. INSTRUCTION LIST PROGRAMMING
- •27.1 INTRODUCTION
- •27.2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •28. FUNCTION BLOCK PROGRAMMING
- •28.1 INTRODUCTION
- •28.2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •29. ANALOG INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
- •29.1 ANALOG INPUTS
- •29.1.1 Analog To Digital Conversions
- •29.1.2 Analog Inputs With a PLC
- •29.2 ANALOG OUTPUTS
- •29.2.1 Analog Outputs With A PLC
- •29.3 DESIGN CASES
- •29.3.1 Oven Temperature Control
- •29.3.2 Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- •29.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •30. CONTINUOUS CONTROL
- •30.1 CONTROLLING CONTINUOUS SYSTEMS
- •30.2 CONTROLLING DISCRETE SYSTEMS
- •30.3 CONTROL SYSTEMS
- •30.3.1 PID Control Systems
- •30.3.1.1 - PID Control With a PLC
- •30.4 DESIGN CASES
- •30.4.1 Temperature Controller
- •30.5 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •31. PLC DATA COMMUNICATION
- •31.1 COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS CATEGORIES
- •31.2 THE HISTORY
- •31.3 WITH PLCs
- •31.4 SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS
- •31.4.1.1 - ASCII Functions
- •31.4.2 ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
- •31.5 PARALLEL
- •31.6 NETWORKS
- •31.6.1 Introduction
- •31.6.2 OSI Network Model
- •31.6.2.1 - Physical Layer
- •31.6.2.2 - Data Link Layer
- •31.6.2.3 - Network Layer
- •31.6.2.4 - Transport Layer
- •31.6.2.5 - Session Layer
- •31.6.2.6 - Presentation Layer
- •31.6.2.7 - Application Layer
- •31.6.2.8 - Open Systems
- •31.6.2.9 - Networking Hardware
- •31.7 BUS TYPES
- •31.7.1 Devicenet
- •31.7.2 CANbus
- •31.7.3 Controlnet
- •31.7.4 Profibus
- •31.7.5 Ethernet
- •31.7.6 Proprietary Networks
- •31.7.6.1 - Data Highway
- •31.7.7 Other Network Types
- •31.8 DESIGN CASES
- •31.8.1 PLC Interface To Robots And NC Machines
- •31.9 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •32. HUMAN MACHINE INTERFACES (HMI)
- •32.1 INTRODUCTION
- •32.2 HMI/MMI DESIGN
- •32.3 DESIGN CASES
- •32.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •33. DESIGNING LARGE SYSTEMS
- •33.1 PROGRAMMING
- •33.2 DOCUMENTATION
- •33.3 PLC PROGRAM DESIGN FORMS
- •33.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •34. IMPLEMENTATION
- •34.1 ELECTRICAL
- •34.1.1 Electrical Wiring Diagrams
- •34.1.1.1 - JIC Wiring Symbols
- •34.1.2 Wiring
- •34.1.3 Shielding and Grounding
- •34.2 SAFETY
- •34.2.1 Troubleshooting
- •34.2.2 Forcing Outputs
- •34.2.3 PLC Environment
- •34.2.3.1 - Enclosures
- •35. PROCESS MODELLING
- •35.1 REFERENCES
- •35.2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •36. SELECTING A PLC
- •36.1 SPECIAL I/O MODULES
- •36.2 PLC PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
- •36.3 ISSUES
- •36.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •37. PLC REFERENCES
- •37.1 SUPPLIERS
- •37.2 PROFESSIONAL INTEREST GROUPS
- •37.3 PLC/DISCRETE CONTROL REFERENCES
- •38. USING THE OMRON DEMO PACKAGE
- •38.1 OVERVIEW
- •38.1.1 Installation
- •38.1.2 Basic Use
- •38.1.3 Connecting to the PLC
- •38.2 REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OMRON PLC DEMO SOFTWARE
- •39. INDUSTRIAL ROBOTICS
- •39.1 INTRODUCTION
- •39.1.1 Basic Terms
- •39.1.2 Positioning Concepts
- •39.1.2.1 - Accuracy and Repeatability
- •39.1.2.2 - Control Resolution
- •39.1.2.3 - Payload
- •39.2 ROBOT TYPES
- •39.2.1 Basic Robotic Systems
- •39.2.2 Types of Robots
- •39.2.2.1 - Robotic Arms
- •39.2.2.2 - Autonomous/Mobile Robots
- •39.2.2.2.1 - Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
- •39.2.3 Commercial Robots
- •39.2.3.1 - Seiko RT 3000 Manipulator
- •39.2.3.2 - DARL Programs
- •39.2.3.2.1 - Language Examples
- •39.2.3.2.2 - Commands Summary
- •39.2.3.3 - Mitsubishi RV-M1 Manipulator
- •39.2.3.4 - Movemaster Programs
- •39.2.3.4.1 - Language Examples
- •39.2.3.4.2 - Command Summary
- •39.2.3.5 - IBM 7535 Manipulator
- •39.2.3.6 - AML Programs
- •39.2.3.7 - ASEA IRB-1000
- •39.2.4 Unimation Puma (360, 550, 560 Series)
- •39.3 ROBOT APPLICATIONS
- •39.3.1 Overview
- •39.3.2 Spray Painting and Finishing
- •39.3.3 Welding
- •39.3.4 Assembly
- •39.3.5 Belt Based Material Transfer
- •39.4 END OF ARM TOOLING (EOAT)
- •39.4.1 EOAT Design
- •39.4.2 Gripper Mechanisms
- •39.4.2.1 - Vacuum grippers
- •39.4.3 Magnetic Grippers
- •39.4.3.1 - Adhesive Grippers
- •39.4.4 Expanding Grippers
- •39.4.5 Other Types Of Grippers
- •39.5 ADVANCED TOPICS
- •39.5.1 Simulation/Off-line Programming
- •39.6 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •40. ROBOTIC PATH PLANNING METHODS
- •40.1 INTRODUCTION:
- •40.1.1 ROBOT APPLICATIONS
- •40.1.2 ROBOTIC CONSTRAINTS
- •40.1.3 THE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM OF PATH PLANNERS
- •40.1.4 EVALUATION OF PATH PLANNERS
- •40.2 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
- •40.2.1 PROBLEM DIMENSIONALITY
- •40.2.2 2D MOBILITY PROBLEM
- •40.2.2.1 - 2.5D HEIGHT PROBLEM
- •40.2.2.2 - 3D SPACE PROBLEM
- •40.2.3 COLLISION AVOIDANCE
- •40.2.4 MULTILINK
- •40.2.5 ROTATIONS
- •40.2.6 OBSTACLE MOTION PROBLEM
- •40.2.7 ROBOT COORDINATION
- •40.2.8 INTERACTIVE PROGRAMMING
- •40.3 SETUP EVALUATION CRITERIA
- •40.3.1 INFORMATION SOURCE
- •40.3.1.1 - KNOWLEDGE BASED PLANNING (A PRIORI)
- •40.3.1.2 - SENSOR BASED PLANNING (A POSTIERI)
- •40.3.2 WORLD MODELLING
- •40.4 METHOD EVALUATION CRITERIA
- •40.4.1 PATH PLANNING STRATEGIES
- •40.4.1.1 - BASIC PATH PLANNERS (A PRIORI)
- •40.4.1.2 - HYBRID PATH PLANNERS (A PRIORI)
- •40.4.1.3 - TRAJECTORY PATH PLANNING (A POSTIERI)
- •40.4.1.4 - HIERARCHICAL PLANNERS (A PRIORI & A POSTIERI)
- •40.4.1.5 - DYNAMIC PLANNERS (A PRIORI & A POSTIERI)
- •40.4.1.6 - OFF-LINE PROGRAMMING
- •40.4.1.7 - ON-LINE PROGRAMMING
- •40.4.2 PATH PLANNING METHODS
- •40.4.3 OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES
- •40.4.3.1 - SPATIAL PLANNING
- •40.4.3.2 - TRANSFORMED SPACE
- •40.4.3.3 - FIELD METHODS
- •40.4.3.4 - NEW AND ADVANCED TOPICS
- •40.4.4 INTERNAL REPRESENTATIONS
- •40.4.5 MINIMIZATION OF PATH COSTS
- •40.4.6 LIMITATIONS IN PATH PLANNING
- •40.4.7 RESULTS FROM PATH PLANNERS
- •40.5 IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION CRITERIA
- •40.5.1 COMPUTATIONAL TIME
- •40.5.2 TESTING OF PATH PLANNERS
- •40.6 OTHER AREAS OF INTEREST
- •40.6.1 ERRORS
- •40.6.2 RESOLUTION OF ENVIRONMENT REPRESENTAION
- •40.7 COMPARISONS
- •40.8 CONCLUSIONS
- •40.9 APPENDIX A - OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES
- •40.9.1 OPTIMIZATION : VELOCITY
- •40.9.2 OPTIMIZATION : GEOMETRICAL
- •40.9.3 OPTIMIZATION : PATH REFINEMENT
- •40.9.4 OPTIMIZATION : MOVING OBSTACLES
- •40.9.5 OPTIMIZATION : SENSOR BASED
- •40.9.6 OPTIMIZATION : ENERGY
- •40.10 APPENDIX B - SPATIAL PLANNING
- •40.10.1 SPATIAL PLANNING : SWEPT VOLUME
- •40.10.2 SPATIAL PLANNING : OPTIMIZATION
- •40.10.3 SPATIAL PLANNING : GENERALIZED CONES
- •40.10.4 SPATIAL PLANNING : FREEWAYS
- •40.10.5 SPATIAL PLANNING : OCT-TREE
- •40.10.6 SPATIAL PLANNING : VORONOI DIAGRAMS
- •40.10.7 SPATIAL PLANNING : GENERAL INTEREST
- •40.10.8 SPATIAL PLANNING - VGRAPHS
- •40.11 APPENDIX C - TRANSFORMED SPACE
- •40.11.1 TRANSFORMED SPACE : CARTESIAN CONFIGURATION SPACE
- •40.11.1.1 - TRANSFORMED SPACE :
- •40.11.2 TRANSFORMED SPACE : JOINT CONFIGURATION SPACE
- •40.11.3 TRANSFORMED SPACE : OCT-TREES
- •40.11.4 TRANSFORMED SPACE : CONSTRAINT SPACE
- •40.11.5 TRANSFORMED SPACE : VISION BASED
- •40.11.6 TRANSFORMED SPACE : GENERAL INTEREST
- •40.12 APPENDIX D - FIELD METHODS
- •40.12.1 SPATIAL PLANNING : STEEPEST DESCENT
- •40.12.2 SPATIAL PLANNING : POTENTIAL FIELD METHOD
- •40.13 APPENDIX E - NEW AND ADVANCED TOPICS
- •40.13.1 ADVANCED TOPICS : DUAL MANIPULATOR COOPERATION
- •40.13.2 ADVANCED TOPICS : A POSTIERI PATH PLANNER
- •40.13.3 NEW TOPICS - SLACK VARIABLES
- •40.14 REFERENCES:
- •41. ROBOTIC MECHANISMS
- •41.1 KINEMATICS
- •41.1.1 Basic Terms
- •41.1.2 Kinematics
- •41.1.2.1 - Geometry Methods for Forward Kinematics
- •41.1.2.2 - Geometry Methods for Inverse Kinematics
- •41.2 MECHANISMS
- •41.3 ACTUATORS
- •41.3.1 Modeling the Robot
- •41.4 PATH PLANNING
- •41.4.1 Slew Motion
- •41.4.1.1 - Joint Interpolated Motion
- •41.4.1.2 - Straight-line motion
- •41.4.2 Computer Control of Robot Paths (Incremental Interpolation)
- •41.5 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •42. MOTION PLANNING AND TRAJECTORY CONTROL
- •42.1 TRAJECTORY CONTROL
- •42.1.1 Resolved Rate Motion Control
- •42.1.2 Cartesian Motion System
- •42.1.3 Model Reference Adaptive Control (MRAC)
- •42.1.4 Digital Control System
- •42.2 PATH PLANNING
- •42.2.1 Slew Motion
- •42.2.1.1 - Joint Interpolated Motion
- •42.2.1.2 - Straight-line motion
- •42.3 MOTION CONTROLLERS
- •42.3.1 Computer Control of Robot Paths (Incremental Interpolation)
- •42.4 SPECIAL ISSUES
- •42.4.1 Optimal Motion
- •42.4.2 Singularities
- •42.5 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •42.6 MICROBOT OVERVIEW
- •42.7 CRS PLUS ROBOT OVERVIEW
- •42.8 BASIC DEMONSTRATION STEPS
- •43. CNC MACHINES
- •43.1 MACHINE AXES
- •43.2 NUMERICAL CONTROL (NC)
- •43.2.1 NC Tapes
- •43.2.2 Computer Numerical Control (CNC)
- •43.2.3 Direct/Distributed Numerical Control (DNC)
- •43.3 EXAMPLES OF EQUIPMENT
- •43.3.1 EMCO PC Turn 50
- •43.3.2 Light Machines Corp. proLIGHT Mill
- •43.4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
- •44. CNC PROGRAMMING
- •44.1 G-CODES
- •44.3 PROPRIETARY NC CODES
- •44.4 GRAPHICAL PART PROGRAMMING
- •44.5 NC CUTTER PATHS
- •44.6 NC CONTROLLERS
- •44.7 PRACTICE PROBLEMS

page 166
emitted from the object.
-Strain Gage - Widely used to indicate torque, force, pressure, and other variables. Output is change in resistance due to strain, which can be converted into voltage.
-Thermistor - Also called a resistance thermometer; an instrument used to measure temperature. Operation is based on change in resistance as a function of temperature.
-Thermocouple - widely used temperature transducer based on the Seebeck effect, in which a junction of two dissimilar metals emits emf related to temperature.
-Turbine Flowmeter - transducer to measure flow rate. Output is pulse train.
-Venturi Tube - device used to measure flow rates.
13.3 ANGULAR POSITION
13.3.1 Potentiometers
•A variable resistor is used to convert an angle or displacement to resistance/voltage.
•These give absolute position readings.
•Linear resistors are used for measuring linear displacement.
•The basic principle of operation is that a moving wiper (sensor input) moves a contact along a resistor. The ends of the resistor are connected to reference voltages. As the wiper moves the potentiometer acts as a voltage divider and produces a voltage proportional to position.
V
Vout=V(a/L)
L
• rotational potentiometers are the most popular. These may be limited to a fixed range either less than 360, or some number of turns.

page 167
V
Vout |
|
θ |
Vout |
---------- |
|
= V θ |
|
|
|
|
max |
•Advantages include,
-typically inexpensive
-easy to use
-very common in a variety of forms, resistances, etc.
•Disadvantages include,
-limited accuracy (there are high cost solutions)
-subject to mechanical wear
13.3.2 Encoders
•An incremental encoder will produce a set of output pulses, and a direction as it is rotated.
•The encoder contains an optical disk with fine windows etched into it. As the encoder shaft is rotated, the etched disk inside rotates. As it rotates various optical sensors are turned on and off.
•There are two basic types,
absolute - the same shaft position will always give the same position reading relative/incremental - these just indicate movement, and they require that other circuits or pro-
grams be used to track position
• How the openings are etched onto the disk determine whether it is absolute or relative.

page 168
sensors read across a single radial line
relative |
|
(quadrature) encoder |
absolute encoder |
|
•In actual encoders there can be thousands of divisions per rotation.
•With an absolute encoder the output is a binary or gray code number.
•A quadrature pulse counter uses two pulses out of phase and deduces distance and direction.

page 169
Quad input A
clockwise rotation
Quad Input B
Note the change as direction 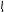 is reversed
is reversed 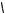
total displacement can be determined by adding/subtracting pulse counts (direction determines add/subtract)
Quad input A
counterclockwise rotation
Quad Input B
To determine direction we can do a simple check. If both are off or on, the first to change state determines direction. Consider a point in the graphs above where both A and B are off. If A is the first input to turn on the encoder is rotating clockwise. If B is the first to turn on the rotation is counterclockwise.
13.3.3 Resolvers
• These use small magnetic coils to detect positions and behave much like relative encoders.
13.3.4 Practice Problems
1. What is the resolution of an absolute optical encoder that has six tracks? nine tracks? twelve
