
447
.pdfФедеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования «Пермская государственная сельскохозяйственная академия имени академика Д.Н. Прянишникова»
Кафедра иностранных языков
Н. И. Никитина
ENGLISH FOR BUSINESS ACTIVITIES
AND BUSINESS NEGOTIATIONS
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК ДЛЯ РАБОТЫ И ДЕЛОВЫХ ПЕРЕГОВОРОВ
Учебно-методическое пособие
Пермь
ИПЦ «ПрокростЪ»
2014
УДК 42 ББК 81ю2 Англ.
Н 624
Рецензенты:
М.С. Шевелева, канд. психол. наук, доцент кафедры иностранных языков НИУ ВШЭ;
Е.Б. Кучина, старший преподаватель кафедры иностранных языков ФГБОУ ВПО Пермская ГСХА.
Н 624. Никитина Н. И.
English for Business Activities and Business Negotiations (Английский язык для работы и деловых переговоров): учебно-методическое пособие / Н.И. Никитина; федеральное гос. бюджетное образоват. учреждение высшего проф. образов. «Пермская гос. с.-х. акад. им. акад. Д.Н. Прянишникова». – Пермь: ИПЦ
«Прокростъ», 2014. –– 98 с.
Пособие содержит материалы о деятельности компаний и современной практике деловых переговоров и включает лексико-грамматические тесты и краткий грамматический справочник с упражнениями.
Учебно-методическое пособие по дисциплинам «Деловой иностранный язык» и «Деловые переговоры и деловая переписка на иностранном языке» предназначено для студентов второго курса экономического факультета.
УДК 42 ББК 81ю2 Англ.
Печатается по решению методической комиссии факультета агротехнологий и лесного хозяйства Пермской государственной сельскохозяйственной академии имени Д.Н.Прянишникова (протокол № 15 от 20 мая 2014 г)
Учебное издание
Никитина Наталья Ивановна
ENGLISH FOR BUSINESS ACTIVITIES
AND BUSINESS NEGOTIATIONS
(Английский язык для работы и деловых переговоров)
Учебно-методическое пособие
Подписано в печать 4.09.2014. Формат 60×841/16 Усл. печ. л. 6,13. Тираж 100 экз. Заказ № 65
ИПЦ «ПрокростЪ»
Пермской государственной сельскохозяйственной академии имени академика Д.Н. Прянишникова,
614000, Россия, г. Пермь, ул. Петропавловская,23
тел. 210-35-34
© ИПЦ «Прокростъ», 2014 © ФГБОУ ВПО Пермская ГСХА, 2014 © Н.И. Никитина, 2014
2
Предисловие
Учебно-методическое пособие составлено в соответствии с программами по дисциплинам «Деловой иностранный язык» и «Деловые переговоры и деловая
переписка на иностранном языке» |
по ФГОС III поколения |
|
для неязыковых вузов. Пособие |
предназначено |
для |
студентов второго курса факультета экономики, финансов и коммерции, и также может быть использовано для преподавания предмета «Коммуникативный английский язык» на третьем курсе факультета прикладной информатики
очного и заочного отделений. |
|
|
|
Целью |
пособия |
является |
формирование |
социокультурной |
и коммуникативной |
компетенций для |
|
совершенствования и достижения успеха в профессиональной деятельности.
Тематика пособия включает материалы о типах и структуре компаний; основам менеджмента в деятельности компаний; подготовке к деловым переговорам и алгоритме ведения деловых переговоров; контрактах, типах контрактов, трудностях в ходе обсуждения положений контрактов.
Включенные в пособие материалы являются аутентичными текстами из современных учебных пособий по бизнесу, журналов и интернет-сайтов. Все тексты снабжены краткими словарями, которые позволяют использовать их на уроке без предварительной подготовки.
Практические задания пособия направлены на формирование и закрепление лексико-грамматических навыков и способствуют развитию речевых умений, как в
устной, так и в письменной речи. |
|
|
Коммуникативная |
направленность |
пособия |
обеспечивается включением |
в него большого |
количества |
|
3 |
|
клише, необходимых в деловом общении на всех его этапах от обсуждения плана до подписания контракта. Предлагаемые клише позволяют управлять процессами подготовки к переговорам и вести переговоры конструктивно и в режиме толерантности.
Каждая глава пособия достаточно самостоятельна и может использоваться отдельно. В каждом разделе имеются тексты различного уровня сложности, что позволяет использовать их для работы со студентами разного уровня подготовки
Пособие снабжено кратким грамматическим справочником, содержащим три грамматических конструкции, обладающие большой речевой частотностью в английском языке, но представляющие наибольшую трудность для студентов при изучении английского языка: сложное дополнение, сложное причастие и инфинитив в функции определения.
Тесты, включенные в пособие, позволяют проверить уровень усвоения студентами навыков и умений, необходимых для делового общения в англоязычной среде.
4
Unit 1 The Changing Environment of the Economics
Text 1
The Changing Environment of Economics
Vocabulary
accordingly (adv.) - |
in spite of – несмотря на |
соответственно |
output (n.)– выпуск |
adjust (v.) - регулировать |
(продукции) |
average (adj.) - средний |
interest rate – процентная |
avoid (v.) - избегать |
ставка |
compete (v.) -завершать |
have effect = have impact - |
currently (adv.) – в текущий |
воздействовать |
момент |
make the most = make |
decline (v.) – снижаться, |
maximum |
падать |
revenues (n.pl.) - доходы |
demand (n.) - спрос |
retail chains – сеть |
estimate (v.) - оценивать |
розничной торговли |
expenses (n.pl.) - расходы |
spot (v.) = spotlight – |
fluency (n.)– свободное |
высвечивать, выделять |
владение |
growth rate – темпы роста |
steadily (adv.) - устойчиво |
|
|
|
Managers make decisions in a changing world. They have to make decisions in ever changing business conditions which create uncertainties. Managers must
choose investment programs,
set prices for their products,
design advertising campaigns and do it all in spite of the uncertainties.
The economic conditions are changing constantly and there is no end to this process. These changes can be grouped into three main sections:
5
economic,
demographic and
social.
The combinations of all three make up the socio-economic
context in which decision-makers, people in decision-making positions, have to act.
Economic changes in brief. The profitability of any business, private or belonging and controlled by the state, is closely connected with the health of the national economy. Economic changes, say, changes in output, prices, interest rates, have a powerful effect on business.
Can businesses affect the direction of the economic development? Even the largest firms, like general Motors, are unable to do it. So, we have to say that economic changes are uncontrollable. But to make the most of what they actually can smart managers must understand how the changes of the economy affect their revenues and expenses (be it a private business or a state institution) and act accordingly.
Demographic changes. Demography is a human science that studies characteristics of human population. These characteristics include such factors as age and the family structure, for instance. Demographic changes can have dramatic effect on the market on consumer goods and services.
After the post war boom which finished in 1955 the growth rate of the population has declined in the USA. Currently the population in the country is increasing at the rate of 1 percent a year. This means that the demand for all new products will not be growing constantly. With less buyers companies will have to compete for their customers, and one company‟s success may come to the other company‟s failure.
6
In every country a certain percentage of the population is constantly on the move migrating from one part of the country to another in search of jobs and better standard of living. These moves are called regional shifts. In the USA in the period from 1955 to 2000 two of five American families moved to a new residence.
Besides, there is urban migration when people move from big cities to small towns, from down town to the suburbs. These urban migration patterns will significantly affect business decisions. The fact that small towns are growing much faster than big cities makes retail chains open their new stores there. That move to smaller towns demands new mentality in the decisionmaking process.
Family structure is also a significant factor: the average size of the family is decreasing; people tend to get married later.The population of the developed countries (North America, Western Europe and Japan) is getting older, i.e. the average age of the population is increasing. For the makers of consumer goods and other business planners, aging of the populations is a very important factor. They cannot control it, but they can spot it, observe its consequences and adjust their business decisions accordingly.
Social changes. What do social changes imply? These are changes in people attitude to everything around them: from jobs and drinking alcohol to fashions and preferences in studying languages. Such changes can have powerful impact on goods and services that will be demanded in the market place. Social changes include a change in women‟s employment. Fifty percent of the college graduates in the USA are women. What is the outcome of this tendency? Women who concentrate on making careers and reaching financial independence get married later and
7
give birth to fewer children. Does this trend affect their spending habits? It, certainly, does.
Afro-American, Hispanian and Asian minorities are starting to play greater roles on the labor market. In the USA people from these minorities actively advance into such spheres as medicine, law and engineering, where “whites” dominated in the past.
Concern for the environment has become a key element in social changes. The higher level of education in all professional groups has affected drinking habits: people tend to avoid hard liquor preferring milder forms of alcohol like wine and beer. The movement of consumers to protect their rights has changed the practice of buyers‟ and sellers‟ interaction in the market place.
The history of the Philip Morris Company is a good illustration of the impact the social changes have on business activities. Philip Morris is the largest advertiser and the largest manufacturer of cigarettes in the USA. Some thirty years ago when cigarettes manufacturers were not allowed to advertise tobacco on radio and TV, the company switched to food products. Today it is the largest food-processing and food-packaging firm in the country: they get 51% of their revenues from food products. At the same time they continue to sell tobacco in large quantities, but in countries where smoking habits did not change much or change very slowly – in Japan, Eastern Europe and Russia.
A few words about studying languages: in Lithuania more and more people send their children to schools where the Russian language is taught. Why? The Russian language may be helpful when doing business with the neighbor country.
Task 1
Guess the meaning of these words without consulting the dictionary. Pronounce them aloud and you will hear what Russian words, mainly from Latin origin, they mean.
8
necessary - необходимый, |
mental (adj.) -? |
necessitate (v.) - ? |
mentality (n.) -? |
necessity (n.) |
constant (adj.) -? |
control (v.) – ?, |
constantly (adv.) -? |
uncontrollable (adj.) - ? |
age (n.) - возраст , |
group (n.) -?, group (v.) - ? |
aging (n.) -? |
able (adj.) - способный , |
urban migration (adj., n.) - ? |
unable (adj.) -? |
observatory (n.) - ? |
act (n.v.) - ? interaction (n.) |
observe (v.) - ? |
trend (n.) -? |
mentality (n.) -? |
|
|
Task 2
Read the text a second time and answer the questions.
1.Are the economic conditions changing constantly?
2.How many groups of changes are there? How many groups of changes do economists see?
3.What is the socio-economic context?
4.Are changes in economy controllable?
5.Do demographic changes have a great impact on the market for consumer goods and services?
6.What is the main result of the lower population growth rates for the commerce?
7.What do demographic changes include?
8.What do social changes mean?
Task 3
Is it true or false? Put T for true, F for false and I for irrelevant (=was not mentioned in the text).
|
|
T |
F |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Changing business conditions create |
|
|
|
|
uncertainties. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Decision-makers have to act in certain socio- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
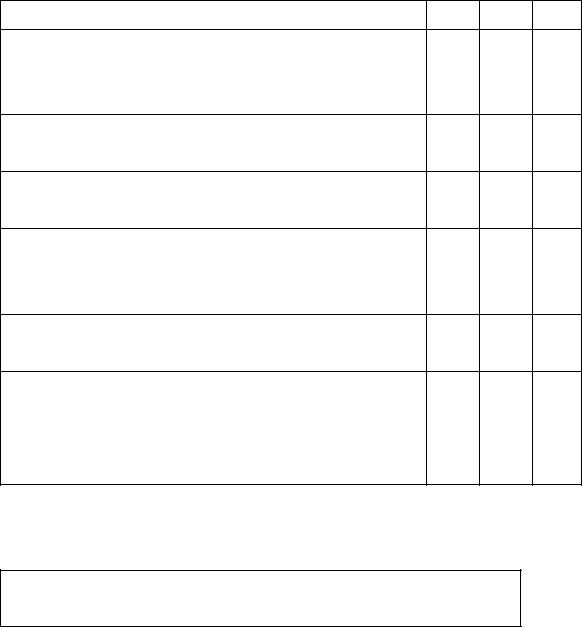
economic context.
3.In spite of all changes you can do what you want: invest any sums, set any prices and plan any advertising campaigns.
4.The market for consumer goods and services is not affected by demographic changes.
5.When the number of customers decrease companies have to compete for them.
6.Changes in drinking habits, tastes and fashions do not affect the market of consumer goods.
7.Increased concern for environment is the key element in social changes.
8.The tobacco manufacturer Philip Morris switched to the sale of food products in the USA but makes large money by selling cigarettes outside USA.
Task 4
Insert the right word from the box.
make the most, affect, growth rate, decline, average, revenues and expenses, in spite of, avoid.
1.We cannot ______ social, economic and demographic changes, they are uncontrollable.
2.Smart managers in all sphere of economy try to foresee and act accordingly ______ uncontrollable changes in economy.
3.Decrease in the ______ of the population cause the fall of the demand for the consumer goods and the rise of the competition among producers and sellers of those goods.
10
