
- •Chest Imaging
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Educational Support and Funding
- •Acknowledgments
- •Contents
- •Fundamentals > Chest Primer Presentation
- •Chest X-Ray Interpretation Self-Study Instructions
- •Using the RoboChest Website
- •Decision Tree Algorithms to Help Solidify Concepts
- •References
- •Comprehensive Review of Search Patterns
- •Search Pattern Mnemonic
- •Interpretive Approach to CXR
- •Applying the Mnemonic to the Search Pattern
- •Chest Primer Presentation
- •References
- •Introduction and Terminology
- •Chest Imaging Terminology
- •Mach Effect on CXR
- •Trachea and Lungs on CXR
- •Mediastinal Anatomy on CXR
- •The Hilum (Plural: Hila)
- •Pulmonary Arteries and Veins
- •Normal Lung Markings
- •Vessel Size
- •Quiz Yourself: Mediastinum Lines, Edges
- •Shoulder Anatomy
- •Reference
- •Abnormal Lung Parenchyma
- •Mass
- •Mass Considerations
- •Size
- •Mass Characteristics
- •Malignancy
- •Case 4.1
- •Metastatic
- •Case 4.2
- •Bronchial Carcinoid
- •Radiological Signs
- •Case 4.3
- •Granulomatous Disease
- •Infectious Granulomatous Disease
- •Case 4.4
- •Non-infectious Granulomatous Disease
- •Benign Neoplasm
- •Hamartoma
- •Case 4.6
- •Congenital Abnormality
- •Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations
- •Case 4.7
- •Consolidation
- •Consolidative Radiological Findings/Distribution
- •Consolidative Model
- •Blood (Hemorrhage)
- •Case 4.8
- •Pus (Exudate)
- •Case 4.9
- •Case 4.10
- •Water (Transudate)
- •Pulmonary Edema
- •Case 4.11
- •Case 4.12
- •Protein (Secretions)
- •Case 4.13 (see Figs. 4.38 and 4.39)
- •Cells (Malignancy)
- •Interstitial
- •Radiological Signs
- •Linear Form: Lines
- •Case 4.14
- •Nodular Form: Dots
- •Case 4.15
- •Reticulo-Nodular Form
- •Pneumoconiosis
- •Case 4.16
- •Case 4.17
- •Destructive Fibrotic Lung
- •Case 4.18
- •Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- •Case 4.19
- •Vascular Pattern
- •Normal Pulmonary Vascular Anatomic Review
- •Radiological Signs in the Vascular Pattern
- •Mechanism
- •Vascular Examples
- •Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
- •Case 4.20
- •Pulmonary Venous Congestion
- •Pulmonary Venous Congestion: Edema
- •Emphysema
- •Airway (Bronchial) Patterns
- •Complete Obstruction
- •Lobar Atelectasis (Collapse)
- •Signs
- •Lobar Atelectasis Patterns
- •Complete Obstruction: Case Study
- •Partial Obstruction
- •Radiological Signs
- •Bronchial Wall Thickening
- •Bronchial Wall Thickening Causes
- •Bronchial Wall Thickening Model
- •Bronchiolar
- •Case 4.21
- •References
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Case 5.1
- •Technique and Positioning Revisited
- •Case 5.2
- •Comparison of Effusions over Time
- •Loculated Fluid/Pseudotumor
- •Case 5.3
- •Case 5.4
- •Thickening
- •Pneumothorax
- •Fluid and Air
- •Analogous Model
- •References
- •Anterior Mediastinal Mass
- •Case 6.1
- •Middle Mediastinal Mass
- •Posterior Mediastinal Mass
- •Case 6.2
- •Mediastinal Enlargement
- •Case 6.3
- •Reference
- •Case 7.1
- •Lines and Tubes
- •References
- •Appendix
- •Appendix 1: Glossary and Abbreviations
- •Appendix 2: Sources and Additional References
- •Text Sources
- •Image Sources
- •Additional References
- •Chest Imaging References
- •Chest Imaging Online References
- •Index
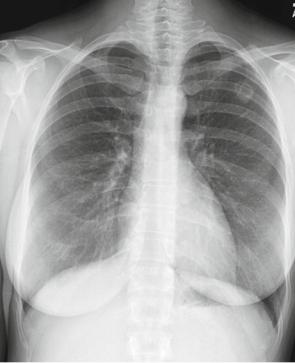
44 |
4 Abnormal Lung Patterns |
Fig. 4.13 CXR of infectious granulomatous disease
Infectious Granulomatous Disease
Infectious granulomatous diseases are frequently identified as nodules (or mass) on a CXR. This can happen with the following diseases.
•Tuberculosis
•Atypical mycobacterial diseases – especially Mycobacterium Avium-Intracellular (MAI)
•Fungal diseases
–Coccidioidomycosis
–Blastomycosis (North American and South American)
–Cryptococcosis
–Sporotrichosis
•Bacterial diseases, nocardiosis and/or actinomycosis
Case 4.4
The following case (Figs. 4.13 – 4.15) presents a 28-year-old female who had a CXR to monitor a preexisting lesion, though she was asymptomatic at the time of the CXR. She lived in central California.

Mass |
45 |
Fig. 4.14 Lateral CXR of infectious granulomatous disease
Findings: Opacity with central lucency in Left Upper Lobe posteriorly. Pattern: Mass, cavitary.
Differential Diagnosis
Since cavitary, consider the CAVITARY mnemonic differential. Wegener’s granulomatosis can appear just like this.
The standard mass differential:
•Malignancy
•Granulomatous
•Inflammation
•Benign neoplasm
•Congenital
Diagnosis: Coccidiomycosis.
In this case, history helped narrow the diagnosis further, as the patient grew up in the San Joaquin River valley: Coccidiomycosis is also known as San Joaquin Valley Fever.
Signs: Fever, cervical adenopathy, skin lesions, pleural effusion, friction rub, pulmonary rales.
