
Елохова.Профессиональный английский язык. Учебно-методическое
.pdfUnit II. Power Engineering
Text 1
Power Engineering Components
Modern Power Engineering deals with the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity as well as the design of a range of related devices. These include transformers, electric generators, electric motors and power electronics.
The power grid is an electrical network that connects a variety of electric generators to the users of electric power. Users purchase electricity from the grid avoiding the costly exercise of having to generate their own. Power engineers may work on the design and maintenance of the power grid as well as the power systems that connect to it. Such systems are called on-grid power systems and may supply the grid with additional power, draw power from the grid or do both.
Power engineers may also work on systems that do not connect to the grid. These systems are called off-grid power systems and may be used in preference to on-grid systems for a variety of reasons. For example, in remote locations it may be cheaper for a mine to generate its own power rather than pay for connection to the grid and in most mobile applications connection to the grid is simply not practical.
Today, most grids adopt three-phase electric power with alternating power that can be generated, transformed and used. Often the power is split before it reaches residential customers whose low-power appliances rely upon single-phase electric power. However, many larger industries and organizations still prefer to receive the three-phase power directly because it can be used to drive highly efficient electric motors such as three-phase induction motors.
Transformers play an important role in power transmission because they allow power to be converted to and from higher voltages. This is important because higher voltages suffer less power loss during transmission. This is because higher voltages allow for lower current to deliver the same amount of power, as power is the product of the two quantities: current and voltage. Thus, as the voltage steps up, the current steps down. It is the current flowing through the components that result in both the losses and the subsequent heating. These losses, appearing in the form of heat, are equal to the current squared times the electrical resistance through which the current flows, so as the voltage goes up the losses are dramatically reduced.
For these reasons, electrical substations exist throughout power grids to convert power to higher voltages before transmission and to lower voltages suitable for appliances after transmission.
Exercise 1. Answer the questions:
1.What does power engineering deal with?
2.What is the power grid for?
3.How can you call the systems which are not connected to the grid?
21
4.What is the standard adaptation of the most grids?
5.Where are single-phase and three-phase electric powers used?
6.What are transformers for?
7.What is the aim of increasing voltage?
8.How can electric power be converted higher voltage?
Exercise 2. Decide if the statements are True or False:
1.The power grid is an electrical network that connects a variety of electric generators to the suppliers of electric power.
2.Users purchase electricity from the grid cannot avoid the costly exercise of having to generate their own.
3.Transforming is important because higher voltages suffer less power loss during transmission.
4.To drive highly efficient electric motors such as induction motors you need three-phase power.
5.The losses, appearing in the form of heat, are equal to the current squared times the electrical resistance through which the current flows.
Exercise 3. Complete the sentences with the words:
electric current, neutral wire, alternating currents, transfer, three-phase system, single-phase appliances
In a,____________ 1 three circuit conductors carry three __________ 2 (of the same frequency) which reach their instantaneous peak values at different times. Taking one conductor as the reference, the other two currents are delayed in time by one-third and two-thirds of one cycle of the _______3. This delay between phases has the effect of giving constant power __________ 4 over each cycle of the current and also makes it possible to produce a rotating magnetic field in an electric motor.
Three-phase systems may have a ________ 5. A neutral wire allows the threephase system to use a higher voltage while still supporting lower-voltage _______
6. In high-voltage distribution situations, it is common not to have a neutral wire as the loads can simply be connected between phases (phase-phase connection).
Exercise 4. Complete the sentences with the necessary forms of the words from the right:
Single-phase loads may _______ 1 to a three- |
1. connect |
phase system in two ways. A load may be |
|
connected across two of the three phase _____ 2 |
2. conduct |
or a load can be connected from a live phase |
|
conductor to the system neutral. Single-phase |
|
loads should be distributed ______ 3 between the |
3. even |
phases of the three-phase system for efficient use |
|
of the supply transformer and supply conductors. |
|
22 |
|
Where the line-to-neutral voltage is a standard |
|
______ 4 voltage (for example in a 230 V/400 |
4. utilize |
V system), individual single-phase utility |
|
customers or loads may each be connected to a |
|
______ 5 phase of the supply. Where the line-to- |
5. differ |
neutral voltage is not a common utilization |
|
voltage, for example in a 347/600 V system, |
|
single-phase loads must be supplied by |
|
individual step-down _______ 6. |
6. transform |
Exercise 5. Complete the sentences with the words:
utilize, generators, distribution systems, network, transmission system, components, industry
An electric power system (or simply power system) is a … of electrical … used to supply, transmit and … electric power. The quintessential example of an electric power system is the network that supplies a region’s homes and industry with power – for sizable regions, this power system is known as the grid and can be broadly divided into the … that supply the power, the … that carries the power from the generating centers to the load centers and the … that feeds the power to nearby homes and industries. Smaller power systems are also found in …, hospitals, commercial buildings and homes.
Text 3
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical power supply. It now covers a range of subtopics including power, electronics, control systems, signal processing and telecommunications.
Electrical engineering may include electronic engineering. Where a distinction is made, electrical engineering is considered to deal with the problems associated with large-scale electrical systems such as power transmission and motor control, whereas electronic engineering deals with the study of small-scale electronic systems including computers and integrated circuits. Alternatively, electrical engineers are usually concerned with using electricity to transmit energy, while electronic engineers are concerned with using electricity to process information.
Electrical engineers design new and better electronics. They also test equipment and solve problems. A project starts by deciding what the new electronics will do. Then, the engineer designs the circuits and other parts of the electronics. Later, the engineers test their designs and make them better. Many
23
projects don’t work at first. The engineers have to figure out why and then fix them.
Electrical engineers work on many kinds of products. They might work on cars, robots, cell phone systems, the lighting and wiring in buildings, and radar and navigation systems. Some examples of high-tech projects that electrical and electronics engineers work on are global positioning systems that can pinpoint a car’s location, giant generators that can power entire cities, or a new design for an airplane’s electrical system.
Engineers should be creative, curious, logical, and detail-oriented. They should also be able to work as part of a team.
Exercise 1. Answer the following questions:
1.What is electrical engineering?
2.What subtopics does electrical engineering include?
3.What is the distinction between electrical engineering and electronic engineering?
4.What do electrical engineers deal with?
5.What high-tech projects do electrical engineers work on?
Exercise 2. Match the following:
1.Electrical engineering deals with ….
2.In the late nineteenth century electrical engineering was associated with ….
3.Electrical engineering is considered to deal with ….
4.Electronic engineering deals with the study of ….
5.Electrical and electronics engineers work on ….
6.Electronics engineering systems can ….
a.pinpoint a car’s location..
b.the problems associated with large-scale electrical systems.
c.the electric telegraph and electrical power supply
d.global positioning systems
e.small-scale electronic systems including computers and integrated circuits.
f.the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism.
Exercise 3. Read the text. Choose the best word (A, B or C) for each space (1–8):
What do Electrical Engineers do?
Electrical engineers design computers and incorporate them into 1 … and systems. They design two-way communications systems such as telephones and fiber-optic systems, and one-way communications systems such as radio and television. They design control systems, such as aircraft collision-avoidance systems, and a variety of systems used in medical electronics. Electrical engineers are involved with 2 …, control, and delivery of electric 3 … to homes, offices, and
24
industry. 4 … power lights, heats, and cools working and living space and operates the many devices used in homes and offices. Electrical engineers analyze and interpret computer-aided tomography data, seismic data from earthquakes and well drilling, and data from space probes. The 5 … with systems that educate and entertain, such as computers and computer networks, compact-disk players, and multimedia systems.
The 6 … of communications equipment, control systems, computers, and other devices and processes into reliable, easily understood, and practical systems is a major challenge, which has given rise to the discipline of systems engineering. Electrical 7 … must respond to numerous demands, including signal 8 …, better communications; faster and more reliable transfer of funds, orders, and information in the business world; and the need of medical professionals for access to medical data and advice from all parts of the world.
1. a. devices |
b. circuits |
c. currents |
2. a. correlation |
b. gravitation |
c. generation |
3. a. power |
b. charge |
c. voltage |
4. a. electricity |
b. electric |
c. electronic |
5. a. deal |
b. design |
c. depend |
6. a. correlation |
b. integration |
c. transmission |
7. a. power |
b. equipment |
c. engineering |
8. a. processing |
b. induction |
c. accumulation |
Exercise 4. Discuss the job of a hydroelectric engineer. Use the keys below:
The work of a hydroelectric engineer is concerned with … .
They are involved in … .
They also construct … and conduct … .
A hydroelectric engineer may work for … .
Ultimately an engineer is focused on … .
Unit III. Hydroelectric Engineering
Text 1
Hydroelectric Generating Countries
Worldwide, about 20 % of all electricity is generated by hydropower. Hydroelectric power plants convert the kinetic energy contained in falling water into electricity. The energy in flowing water is ultimately derived from the sun, and is therefore from constantly being renewed. Energy contained in sunlight evaporates water from the oceans and deposits it on land in the form of rain. Differences in land elevation result in rainfall runoff, and allow some of the original solar energy to be captured as hydroelectric power.
25
Hydropower is currently the world’s largest renewable source of electricity, accounting for 6 % of worldwide energy supply or about 15 % of the world’s electricity. In Canada, hydroelectric power is abundant and supplies 60 % of electrical needs. In the United States, hydropower produces enough electricity to serve the needs of 28 million residential customers. Traditionally thought of as a cheap and clean source of electricity, most large hydroelectric schemes being planned today are coming up against a great deal of opposition from environmental groups and native people.
The United States is the second largest producer of hydropower in the world. Canada is number one. Norway produces more than 99 % of its electricity with hydropower. New Zealand uses hydropower for 75 % of its electricity.
Much of the fuel produced in Russia is converted to electricity, about threefourths of which is generated in thermal stations; some two-thirds of thermal generation is from oil and gas. The remaining power output is produced by hydroelectric and nuclear plants. Most of the hydroelectricity comes from huge stations on the Volga, Kama, Ob, Yenisei, Angara and Zeya rivers. Much of
Siberia’s electricity output is transmitted to the European region along high-voltage lines.
Vocabulary:
hydroelectric power plant – гидроэлектростанция to evaporate – испарять
to deposit – осаждаться
to derive from – получать, извлекать to account for – насчитывать abundant – имеющийся в изобилии a great deal of – большое количество native people – коренные жители
Exercise 1. Find the Russian equivalents to the following word combinations:
falling water, ultimately, land elevation, rainfall runoff, energy supply, electrical needs, residential customers
бытовые потребители, потребности в электроэнергии, падающая вода, объем осадков, полностью, поднятие земли, энергоресурсы
Exercise 2. Answer the questions:
1.How much electricity is produced by hydropower?
2.Why is the energy in flowing water being constantly renewed?
3.What country supplies 60% of its electrical needs with hydropower?
4.What is the second largest producer of hydropower in the world?
5.What European countries actively utilize hydroelectric power? Give examples.
6.What can you say about hydropower in Russia?
26

Exercise 3. Complete this text with the words in the box:
hydro power plants with capacities of over, for hydropower production, for the hydro potential, is home to, amounted to, economically feasible, installed capacity of, the most recent dam projects, hydroelectric producer, signed a cooperation agreement to expand
Russia has 102 … 100 MW, making it the fifth in the world … . It is also the second in the world …, yet only 20 % of this potential is developed. Russia … 9 % of the world hydro resources, mostly in Siberia and the country far east. At the end of 2005, the generating capacity from hydro energetic sources in Russia … . 45,700 MW, and an additional 5,648 MW were under construction. The World Energy Council believes that Russia has much potential for using its hydro resources, with theoretical potential of about 2,295 TWh/year, with 852 TWh being … .
The largest dams in Russia are the Sayano-Shushenskaya Dam, which has an … 6,400 MW; the Krasnoyarsk Dam (6,000 MW); the Bratsk Dam (4,500 MW); the Ust-Ilimsk (4,320 MW). Some of … are the Bureya Dam (2010 MW) and the Irganai Dam (800 MW). Several dams, including the Boguchany Dam (1920 MW), are currently under construction. RusHydro is the largest hydroelectric company in
Russia and the second largest … in the world. In October 2010 the China Yangtze
Power, the largest hydropower corporation in China, and the EuroSibEnergo, a
Russian energy company, … hydroelectric energy production in Russia and export energy to China northern territories. The West Siberian Generating Company has plans to start construction of eight mini-hydro power plants in the Altai region before 2015.
Text 2
Facts about Hydropower
Hydropower is clean. It prevents the burning of 22 billion gallons of oil or 120 million tons of coal each year. Hydropower doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or other air pollution. Hydropower leaves behind no waste. Reservoirs formed by hydropower projects have expanded water-based recreation resources, and they support diverse, healthy, and productive fisheries. In fact, catch rates are substantially higher on hydropower reservoirs than natural lakes.
Hydropower is the most efficient way to generate electricity. Modern hydro turbines can convert as much as 90 % of the available energy into electricity. The best fossil fuel plants are only about 50 % efficient.
Hydropower is the leading source of renewable energy. It provides more than 97 % of all electricity generated by renewable sources. Other sources including solar, geothermal, wind and biomass account for less than 3 % of renewable electricity production.
Reservoirs formed by hydroelectric dams provide many water-based recreational opportunities including fishing, water sports, boating, and water fowl hunting. Hydro-operators own a significant amount of land around many reservoirs
27
that is open to the public for uses including hiking, hunting, snowmobiling, and skiing. Hydro-operators provide many recreation facilities at their hydropower projects including boat landings, swimming beaches, restrooms, picnic and fishing areas, nature trails and parking facilities.
Hydroelectric power has always been an important part of the world’s electricity supply, providing reliable, cost-effective electricity, and will continue to do so in the future. Hydropower has environmental impacts which are very different from those fossil fuel power plants. The actual effects of dams and reservoirs on various ecosystems are only now becoming understood. The future of hydroelectric power will depend on future demand for electricity, as well as how societies value the environmental impacts of hydroelectric power compared to the impacts of other sources of electricity.
Exercise 1. Agree or disagree with the following statements:
1.Hydropower is the most efficient way to generate electricity.
2.Hydropower is the leading source of renewable energy.
3.Reservoirs formed by hydropower projects support diverse, healthy and productive fisheries.
Exercise 2. Discuss the following:
1.How do we get electricity from water?
2.Is it possible to use energy from water in your region? Why? Why not?
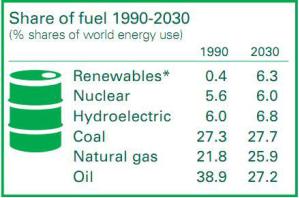
Exercise 3. Analyze the graph (see Fig. 1) and make generalizations about the data. Use the plan given below
Plan:
1.What the graphs shows.
2.What the numbers represent.
3.Make a thesis (a statement or an opinion that is presented with evidence in order to prove that it is true).
4.Support your thesis.
5.Make an appropriate conclusion.
Fig. 1 Energy use map
28
Use the phrases:
The graph/ diagram shows … .
A wide range in the percentage … .
A number of … .
According to the data … .
If to compare … .
We can sum up … .
Text 3
Hydroelectric Power Station
Water power was used to drive machinery long before Polzunov and James Watt harnessed steam to meet man’s needs for useful power.
Modern hydroelectric power stations use water power to turn the machines which generate electricity. The water power may be obtained from small dams in rivers or from enormous sources of water power like those to be found in Russia. However, most of our electricity, that is about 86 per cent, still comes from steam power stations.
In some other countries, such as Norway, Sweden, and Switzerland, more electric energy is produced from water power than from steam. They have been developing large hydroelectric power stations for the past forty years, or so, because they lack a sufficient fuel supply. The tendency, nowadays, even for countries that have large coal resources is to utilize their water power in order to conserve their resources of coal. As a matter of fact, almost one half of the total electric supply of the world comes from water power.
The locality of a hydroelectric power plant depends on natural conditions. The hydroelectric power plant may be located either at the dam or at a considerable distance below. That depends on the desirability of using the head supply at the dam itself or the desirability of getting a greater head. In the latter case, water is conducted through pipes or open channels to a point farther downstream where the natural conditions make a greater head possible.
The design of machines for using water power greatly depends on the nature of the available water supply. In some cases great quantities of water can be taken from a large river with only a few feet head. In other cases, instead of a few feet, we may have a head of several thousands of feet. In general, power may be developed from water by action of its pressure, of its velocity, or by a combination of both.
A hydraulic turbine and a generator are the main equipment in a hydroelectric power station. Hydraulic turbines are the key machines converting the energy of flowing water into mechanical energy. Such turbines have the following principal parts: a runner composed of radial blades mounted on a rotating shaft and a steel casing which houses the runner. There are two types of water turbines, namely, the reaction turbine and the impulse turbine. The reaction turbine is the one for low
29
heads and a small flow. Modified forms of the above turbine are used for medium heads up to 500-600 ft, the shaft being horizontal for the larger heads. High heads, above 500 ft, employ the impulse type turbine. It is the reaction turbine that is most used in Russia.
Speaking of hydraulic turbines, it is interesting to point out that in recent years there has been a great increase in size, capacity, and output of Russian turbines.
Hydropower engineering is developing mainly by constructing high capacity stations integrated into river systems known as cascades.
Exercise 1. Translate the following words:
hydroelectric power station |
a fuel supply |
to generate electricity |
locality |
to be obtained |
at a considerable distance |
a dam |
open channels |
to lack |
an available water supply |
Exercise 2. Find the following equivalents in the text:
охранять/ беречь; воду проводят через трубы или открытые каналы; огромное количество воды; давление; скорость; гидравлическая турбина; базовые технологии/ машины; установленный/ смонтированный; вращающийся шпиндель; металлическая оправа, в которой помещается/ прячется ротор/ рабочее колесо (турбины); активная турбина
Exercise 3. Answer the questions:
1.In what countries is a lot of electric energy produced from water?
2.What does the locality of electric power plants depend on?
3.What does the design of machines for using water depend on? Explain using the text.
4.What are the main equipment of a hydroelectric power plant?
5.What are the two types of water turbines?
6.What are the principal parts of a hydraulic turbine?
Exercise 5. Make up all types of questions to the sentences:
1.Modern hydroelectric power stations use water power to turn the machine which generates electricity.
2.The locality of hydroelectric power plant depends on natural conditions.
Text 4
How Hydroelectric Power Plant Works
So just how do we get electricity from water? Actually, hydroelectric and coal-fired power plants produce electricity in a similar way. In both cases a power source is used to turn a propeller-like piece called a turbine, which then turns a metal shaft in an electric generator, which is the motor that produces electricity. A
30
