
- •HIATAL HERNIA
- •PREAMBLE
- •PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- •Types of Hiatal Hernia
- •Risk factors for Sliding Hiatal Hernia
- •Clinical features of Sliding Hiatal Hernia
- •Complications of Sliding Hiatal Hernia
- •Investigations for Sliding Hiatal Hernia
- •Endoscopic view:
- •Barium swallow demonstrates hiatal hernia:
- •Treatment of Sliding Hiatal Hernia
- •MEDICAL THERAPY
- •SURGICAL THERAPY
- •Anti-reflux procedure e.g Fundoplication
- •Risk factors for Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia
- •Clinical features of paraesophageal hiatal hernia
- •Complications of paraesophageal hiatal hernia
- •Investigation of Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia
- •CT Scan
- •Treatment Of Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia
- •Surgical procedures for P.H.H
- •Anti-reflux procedure e.g Fundoplication
- •Complications Of Surgical treatment
- •Summary

HIATAL HERNIA
Ihor Vynnychenko

PREAMBLE
Hiatal hernia is the protrusion of the stomach upward into the mediastinal cavity through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm.
Normally, a portion of the esophagus and all the stomach are situated in the abdominal cavity.
Normal Anatomy |
Hiatal Hernia |

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Size of hiatus not fixed, narrows with increase in intra- abdominal pressure
Tear of Phrenoesophageal ligament :
is a fibrous layer of connective tissue and maintains the LES within the abdominal cavity
A hiatal hernia compromises reflux barrier
Reduced LES pressure
Reduced esophageal acid clearance
Transient LES relaxation episodes particularly at night time

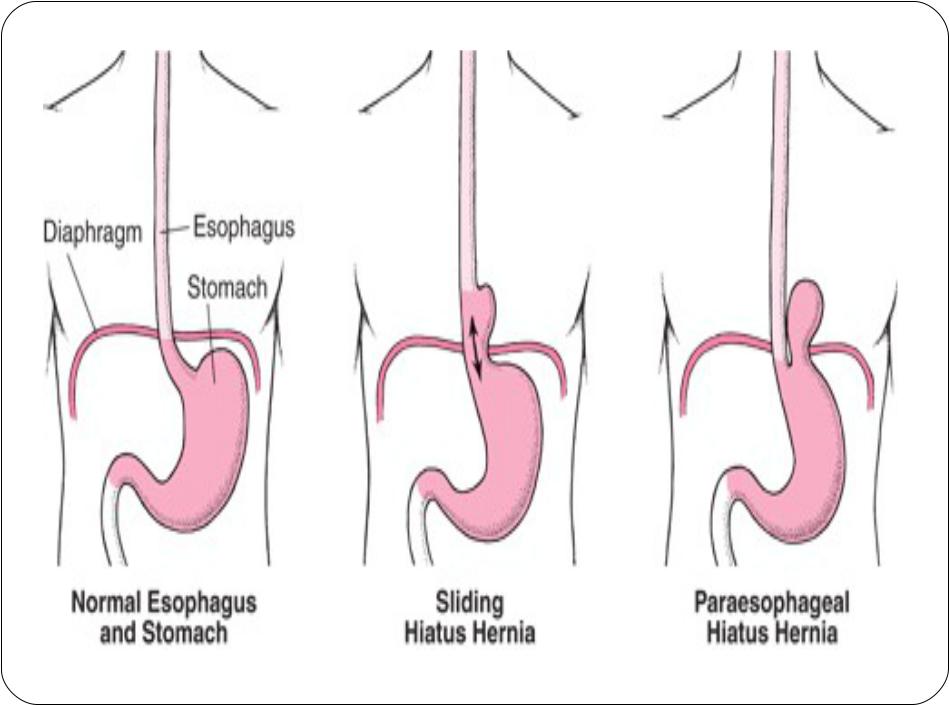
Types of Hiatal Hernia
1. Sliding hiatal hernia:
Herniation of both the stomach and the gastroesophageal(GE) junction into the thorax.
90% of esophageal hernias
2. Paraesophageal hiatal hernia:
Herniation of all or part of the stomach through the esophageal hiatus into the thorax with an undisplaced GE junction
Least common esophageal hernia (<10%)

Risk factors for Sliding Hiatal Hernia
Age
Increased intra-abdominal pressure (e.g. Obesity, pregnancy, coughing, heavy lifting).
Smoking

Clinical features of Sliding Hiatal Hernia
Majority are asymptomatic
Larger hernias frequently associated with Gastroesophageal reflux disease(GERD) due to decreased competence of the Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) .

Complications of Sliding Hiatal Hernia
Most common complication is GERD.
Other complications are rare and are related to reflux
Esophagitis (dysphagia, heartburn)
Consequences of esophagitis ( peptic stricture, Barrett’s esophagus, esophageal carcinoma)
Extra-esophageal complications ( pneumonitis/ pneumonia, asthma, cough, laryngitis)

Investigations for Sliding Hiatal Hernia
Chest X-ray
Barium swallow
Endoscopy
Esophageal manometry (to measure the pressure of LES)
24-48h esophageal pH monitoring to quantify reflux
Gastroscopy with biopsy to rule out cancer and esophagitis

